In App Feedback Scenarios
Guidelines
In App Feedback should come together to create a cohesive experience for your users.
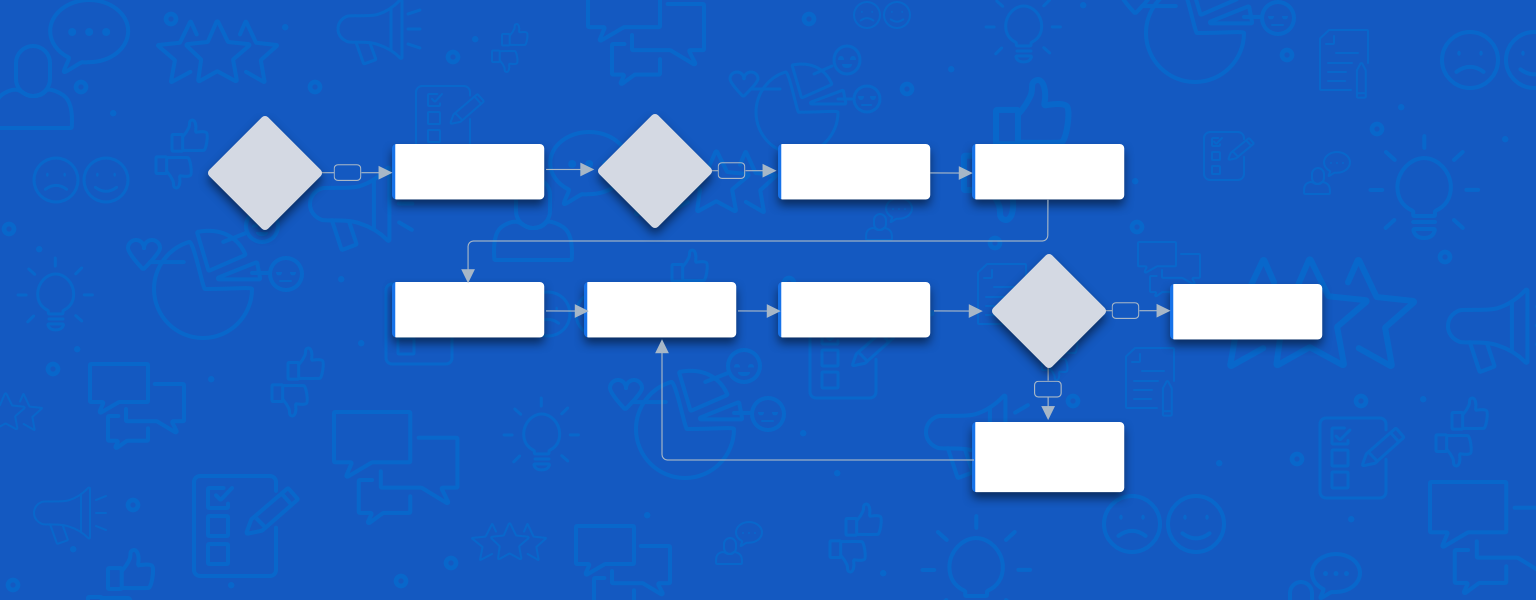
The User Journey
There are many touch points to consider when implementing In App Feedback. The overview of a basic user journey helps to define what that flow will look like for users and ensures that appropriate messaging and follow up is included.
Start using our Design Kits
Open in Figma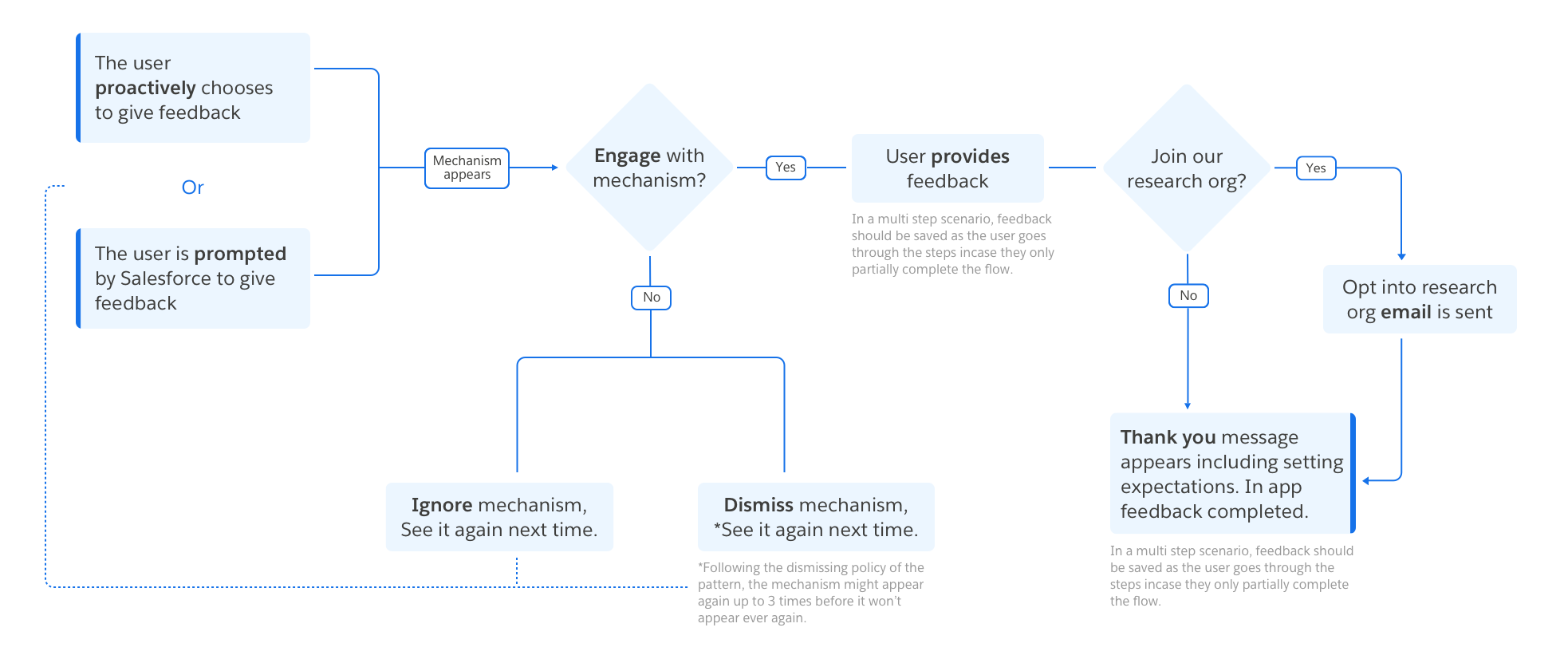
Scenarios
There are two strategies for triggering feedback mechanisms that we'll walk through in these scenarios: user initiated mechanisms and system initiated mechanisms.
User Initiated Mechanisms: These mechanisms persist in the experience, allowing a user to provide feedback at any time through an easy access point. These feedback mechanisms allow you to meet the user where they are on their digital journey to capture a moment to moment reaction. These mechanisms are less interruptive for users than system initiated mechanisms.
System Initiated Mechanisms: Feedback mechanisms initiated by the system are generally reserved for high business impact research questions as they are more interruptive for users. System initiated mechanisms can leverage data to segment the user base and hear from specific audiences. These mechanisms generally do not persist in the experience. Once triggered, a user has the opportunity to provide feedback or may ignore or close the mechanism.
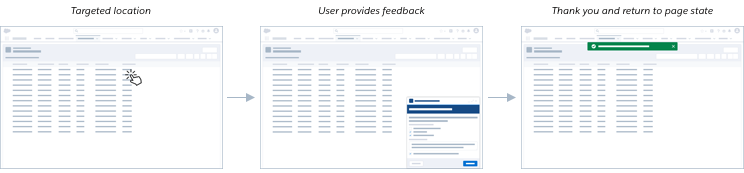
I Want to Hear Feedback From Users About a Specific Feature or Flow.
Strategy: User initiated, in line component on a page
Research purpose
In line components allow you to engage with a specific set of people who visit a page or complete a specific flow, rather than gathering feedback site wide. In line components are great for capturing a reaction from your users about a specific interaction or series of interactions they may have had with the product.
Example questions
- How helpful was this content? 1-5 rating - 1 (not helpful at all) 5 (very helpful)
- Help us understand the factors that informed your score (these can also be a rating scale)
- Time to complete
- Level of difficulty
- Your feedback is valuable to us. We want to know what's working well and what we can improve. Anything else you want us to know? (open text field)
Building the mechanism
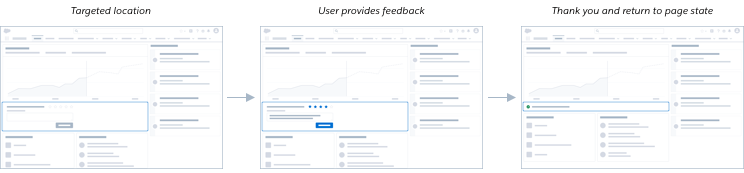
The research purpose in this scenario is more targeted. The feedback launch point should be in a location in line with the content that it references, so that you are able to hear from the specific segment of users who interact with that content. The team can leverage usage data to only show the component to users who meet specific criteria.
Once the user completes the question(s) and submits their feedback, the question may fade away or remain depending on the use case, and success messaging or a thank you message should appear for confirmation to the user. Teams can also use this space to socialize the User Research program if the user wants to continue to give feedback a more consistent basis. Depending on the research purpose, in line components may or may not appear the next time a user navigates to that same page.
I Want to Hear From Users About Their General Experience Using a Product or Set of Products.
Strategy: User initiated, feedback behind a navigation element or icon
Research purpose
Persistent feedback mechanisms have a variety of uses, but mainly serve to give users an opportunity to freely voice their comments, concerns or questions about a specific moment using the product or overall experience. These mechanisms are best for capturing feedback from a broad audience over time.
Example questions
- Your feedback is valuable to us. We want to know what's working well and what we can improve.
- What tasks were you trying to accomplish today? Did [product or service] allow you to successfully accomplish your tasks?
- What are some of the top challenges you are facing with [product or service]? What has been working well for you?
Building the mechanism
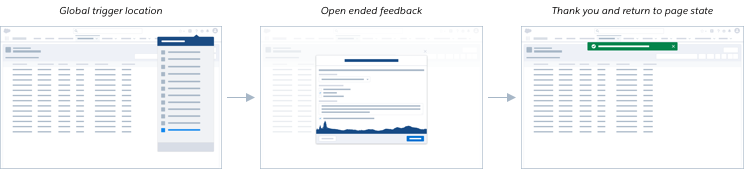
Since the research purpose here is broad and user feedback can relate to a variety of topics, the feedback launch point should be global and accessible on all pages. This can be under a global menu, or any other set of global navigation items that appear on all pages of the application. A user can click on a menu item with a clear title about giving feedback.
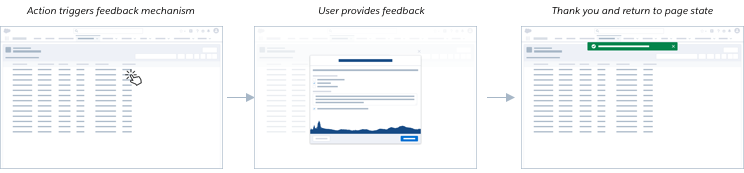
I Want to Collect Feedback From Users Related to a High-Impact Research Initiative About a Task, Flow or General Experience Using the Product(s).
Strategy: System initiated, feedback during a task or flow
Research purpose
System triggered feedback can be intrusive and interruptive for users, so should be reserved for research questions with high importance and high impact.
Example questions
- We're sad to see you leave. Help us understand why?
- Pre populated multiple choice with hypotheses
- Other
- Your feedback is valuable to us. We want to hear what was working well for you and what could be improved to ensure we're creating the best experience for our users.
- Open text field
Building the mechanism
Since any system initiated mechanism could disturb the user or interrupt their workflow, try to choose moments that would be least interruptive to prompt the mechanism. Prompting the mechanism after a user completes a task or at first login before a user has started a task can help to limit the level of interruption to the user. Using containers that do not cover the full screen can also help to limit interruption.
Or
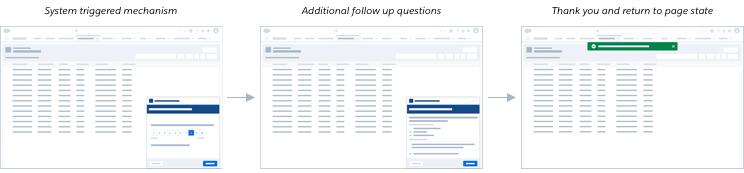
I Want to Collect and Track Net Promoter Scores for my User Base.
Strategy: System initiated, Net Promoter Score survey
Research purpose
The Net Promoter Score metric is used to measure a customer's loyalty to the company by asking the following question:
Example questions
How likely is it that you would recommend our company/product/service to a friend or colleague?
The user can select a score between 0 and 10. This question can be included in other customer surveys, or run as a standalone NPS measurement, with follow up questions related to reasons that may have informed the score.
Building the mechanism
While it is best not to interrupt/prompt users in the middle of the flow, waiting until the final step could introduce biases (namely, over indexing on successful attempts and not hearing from users who abandoned or failed). So, we might consider presenting task based proactive surveys both: (1) At the end of the flow; (2) On exit/while backtracking (e.g., in a 3-step flow the user reaches step 2 but backtracks to step 1 or navigates to a different page).
Next: Research Strategy